
HullRad is an algorithm for calculating hydrodynamic properties of a macromolecule from a structure file.
It provides "A New Determination of [Hydrated] Molecular Dimensions". 1
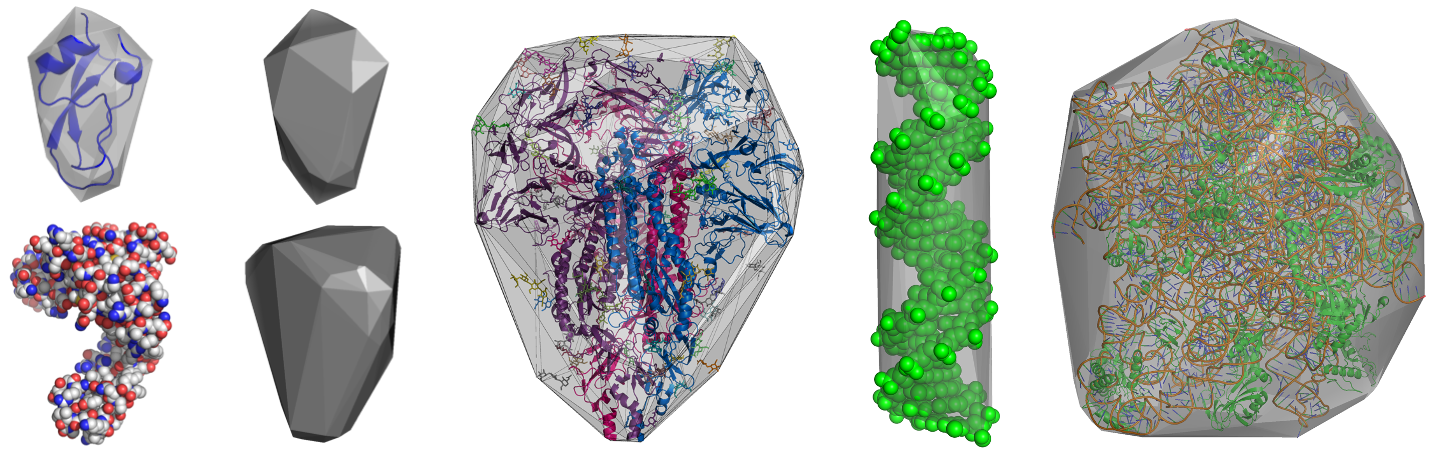
HullRad uses a convex hull model to estimate the hydrodynamic volume of a macromolecule.
The above images show convex hull models of two small proteins, human coronavirus glycosylated spike protein, a DNA duplex, and the bacterial 50s ribosomal subunit.
HullRad is FAST!
Try it out - Download the code or upload your PDB or mmCIF file to the server by clicking on a link at the top of the page.
The latest version of HullRad is Version 10.1 (Oct, 2024). If you use the HullRad script locally you should update NOW by clicking on the link at the top of the page.
HullRadSAS is a modified version of HullRad that provides quantitative macromolecular hydration levels in addition to the standard hydrodynamic properties calculated by the original HullRad. HullRadSAS also provides a hydrated radius of gyration for comparison to SAXS data.
You can learn more about HullRadSAS and download the code by clicking on the link at the top of the page.
A more detailed description of HullRad and HullRadSAS is available as a PDF.
1A nod to Einstein whose PhD thesis title was, "A New Determination of Molecular Dimensions".